AI is increasingly being integrated into actual workflows rather than just chat windows. Teams are using models for ticket summaries, code generation, pull request reviews, and answering internal questions. These workflows create new security challenges. Policies exist, but they are more difficult to implement when fully or semi-autonomous systems make decisions. An AI developer could unintentionally leak sensitive information through an AI assistant, or an autonomous agent could access an API outside the parameters assigned to it.
If an AI model receives seemingly harmless input, it could still generate internal rule violations. AI policy enforcement is the layer that defines the boundaries of acceptable behavior.
What Is AI Policy Enforcement?
AI policy enforcement is the process of defining rules for AI use and automatically applying those rules across data, prompts, tools, and outputs.
In practice, it usually covers four areas:
- Data controls: prevent sensitive data from entering prompts or leaving approved environments
- Access controls: ensure only permitted users and agents can call specific models, tools, or datasets
- Behavior rules: enforce what an AI system is allowed to do, such as which actions it can take in production
- Auditability: record what happened, who initiated it, and what the system produced
When people mention agentic AI policy enforcement, they refer to enforcement that governs tool use and actions, not just text generation.
How AI-Powered Policy Enforcement Works
Most platforms follow a similar pattern. First, you define policies in a form that the system can evaluate. Then enforcement happens at runtime, close to where the AI is used.
A common pipeline looks like this:
- Intercept: get the prompt, context, tool calls, and output.
- Classify: find private information, controlled content, or dangerous intent.
- Choose: allow, block, redact, or need approval.
- Respond: send back either a safe output or an error message that can be acted on.
- Log: keep proof for later checks and reviews.
The enforcement engine relies on a mix of techniques. Some checks are deterministic, such as pattern matching for secrets or customer identifiers. Others use machine learning to detect sensitive business context. The best systems also support policy evaluation based on identity, environment, and risk level.
An example is AI-driven application security policy enforcement.
Benefits of Automated Policy Enforcement for Security Teams
Manual reviews do not scale when AI is embedded in daily work. Automation helps by turning policies into repeatable controls.
Key benefits include:
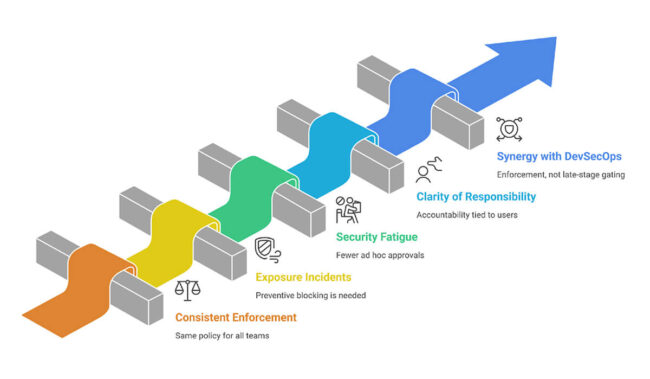
- Consistent Enforcement: the same policy applies to all teams and all tools.
- Prevention of Exposure Incidents: Preventive blocking/redaction can occur before someone sees exposed data.
- Less Security Fatigue: fewer ad hoc approvals, fewer policy discussions in chat threads.
- Greater Clarity of Responsibility: accountability, logs, and decisions tied to users, agents, and actions.
- Improved Synergy with DevSecOps: the activity is the enforcement of controls, not late-stage gating.
There is also a distinct benefit for the security team: it allows them to calibrate controls using actual telemetry rather than having to determine how the AI is deployed.
AI Policy Enforcement vs. Traditional Compliance Methods
While elements of traditional compliance, like periodic audits, documentation, and control checklists, are still necessary, they are slow.
AI policy enforcement shifts compliance left and makes it continuous. Instead of checking a process after the fact, you prevent violations as they occur.
There is also a difference in what is being governed. Compliance programs usually focus on systems and data stores. AI introduces new surfaces, including:
- prompts and context windows
- model outputs and summaries
- tool calls issued by agents
- temporary data created during reasoning steps
That is why a policy enforcement layer is becoming a separate capability, not just an extension of classic security controls.
Implementing AI Policy Enforcement in DevSecOps Workflows
Start small and integrate where developers already work. The goal is to reduce risky behavior without impeding delivery.
Practical steps:
- Define a minimal policy set: Include secrets, personal data, regulated data, and production actions.
- Choose where to enforce: Focus on IDE helpers, chat programs, CI pipelines, API gateways, and agent runtimes.
- Add feedback that is easy for developers to understand: Define what was blocked and how to fix it.
- Log everything needed for audits: Input metadata, policy decisions, and remediation steps.
- Iterate based on results: Change the rules to avoid blocks that make noise.
If you are evaluating AI policy enforcement platforms, look for policy versioning, exception workflows, role-based controls, and robust reporting. Also, check how well it supports real-time enforcement for agents that take actions.
FAQs
1. What regulations does AI policy enforcement help with?
AI policy enforcement can support programs tied to privacy and security obligations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2, depending on your environment. It helps by preventing exposure of sensitive data, enforcing access controls, and generating audit logs that demonstrate consistent control operation across AI-assisted workflows.
2. How does AI policy enforcement reduce false positives?
It reduces false positives by combining context-aware detection with policy logic that considers identity, environment, and data type. Instead of blocking anything that looks suspicious, it can apply targeted actions such as redaction, partial masking, or step-up approvals. Continuous tuning based on telemetry further improves precision.
3. Can AI policy enforcement integrate with CI/CD pipelines?
Of course, numerous teams use enforcement as CI checks, policy gates, or pre-merge validations. For example, the pipeline can generate AI code, scan it for secrets, license risks, or insecure patterns, and then block the build or require a review. This makes enforcement repeatable.
4. What is real-time policy enforcement?
Real-time policy enforcement means policies are evaluated during the AI interaction, not afterward. The system can immediately block, redact, or modify prompts and outputs and prevent agents from executing restricted tool calls. This is critical when AI is used for production operations or sensitive data handling.
5. How does AI policy enforcement improve audit readiness?
It improves audit readiness by generating consistent evidence. Policies, decisions, and logs are captured automatically, with clear links to users, agents, and systems, reducing manual spreadsheet work during audits. It also helps teams demonstrate that controls run continuously, not only during quarterly reviews or annual assessments.